Urology
Urology is a branch of medicine and surgery focused on the diagnosis, treatment, and management of disorders related to the urinary system in both men and women, as well as the male reproductive system. Urologists are the medical professionals who specialize in urology and handle a wide range of conditions affecting the kidneys, bladder, urethra, and male reproductive organs.
Areas of Focus in Urology:
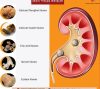
- Kidneys:
- Conditions like kidney stones, chronic kidney disease (CKD), and kidney infections.
- Kidney transplants.
- Bladder:
- Disorders like urinary incontinence (leakage of urine), bladder infections (cystitis), and bladder cancer.
- Urethra:
- Problems such as urethritis (inflammation), strictures (narrowing), and urinary tract infections (UTIs).
- Male Reproductive System:
- Issues like erectile dysfunction (ED), infertility, prostate diseases (e.g., benign prostatic hyperplasia or BPH), and prostate cancer.
- Adrenal Glands:
- Tumors or hormonal imbalances in the adrenal glands that affect the urinary system or overall metabolism.
Common Procedures and Treatments in Urology:
- Cystoscopy: A procedure where a urologist uses a scope to view the bladder and urethra.
- Prostate exams: For assessing prostate health, often in older men, including Digital Rectal Exams (DRE) and PSA (prostate-specific antigen) blood tests.
- Urodynamics: A test to evaluate bladder function and diagnose issues like incontinence or urinary retention.
- Lithotripsy: A non-invasive treatment to break down kidney stones.
- Transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP): A procedure used to treat BPH by removing excess prostate tissue.
Urological Conditions:
- Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs): Infections that can affect any part of the urinary system, more common in women but also affect men, especially older men.
- Erectile Dysfunction (ED): The inability to get or maintain an erection; urologists may treat ED through medications, therapy, or surgery.
- Prostate Cancer: A common cancer in men, often requiring urologists to perform screenings, biopsies, and manage treatments.
- Incontinence: Both stress incontinence (leakage due to physical activity) and urge incontinence (frequent, urgent need to urinate).
- Kidney Stones: Hard deposits that form in the kidneys and may require treatment ranging from dietary changes to surgical procedures for removal.
- Bladder Cancer: A type of cancer that can involve the bladder lining and typically requires specialized urological treatments.
When to See a Urologist:
- Persistent urinary symptoms: Difficulty urinating, frequent urination, blood in urine, or painful urination.
- Kidney stones: If you experience sharp pain, difficulty urinating, or blood in the urine.
- Sexual dysfunction: Erectile problems, low libido, or infertility issues in men.
- Pelvic pain: Unexplained lower abdominal or pelvic discomfort.
- Prostate issues: Symptoms like frequent urination at night or trouble starting urination in men over 50.
Urologists are often trained in both surgical and non-surgical treatments, which makes them essential in the management of both acute and chronic urological conditions.
Would you like more information about any specific urological condition or procedure?
Our Pricing Plan
Meet Our Doctors

Dr. Md. Abid Hossain
MBBS, FCPS (Surgery), MS (Urology), FRCS (Ireland), FRCS (Glasgow)Urology
Make an Appointment